RESOURCES
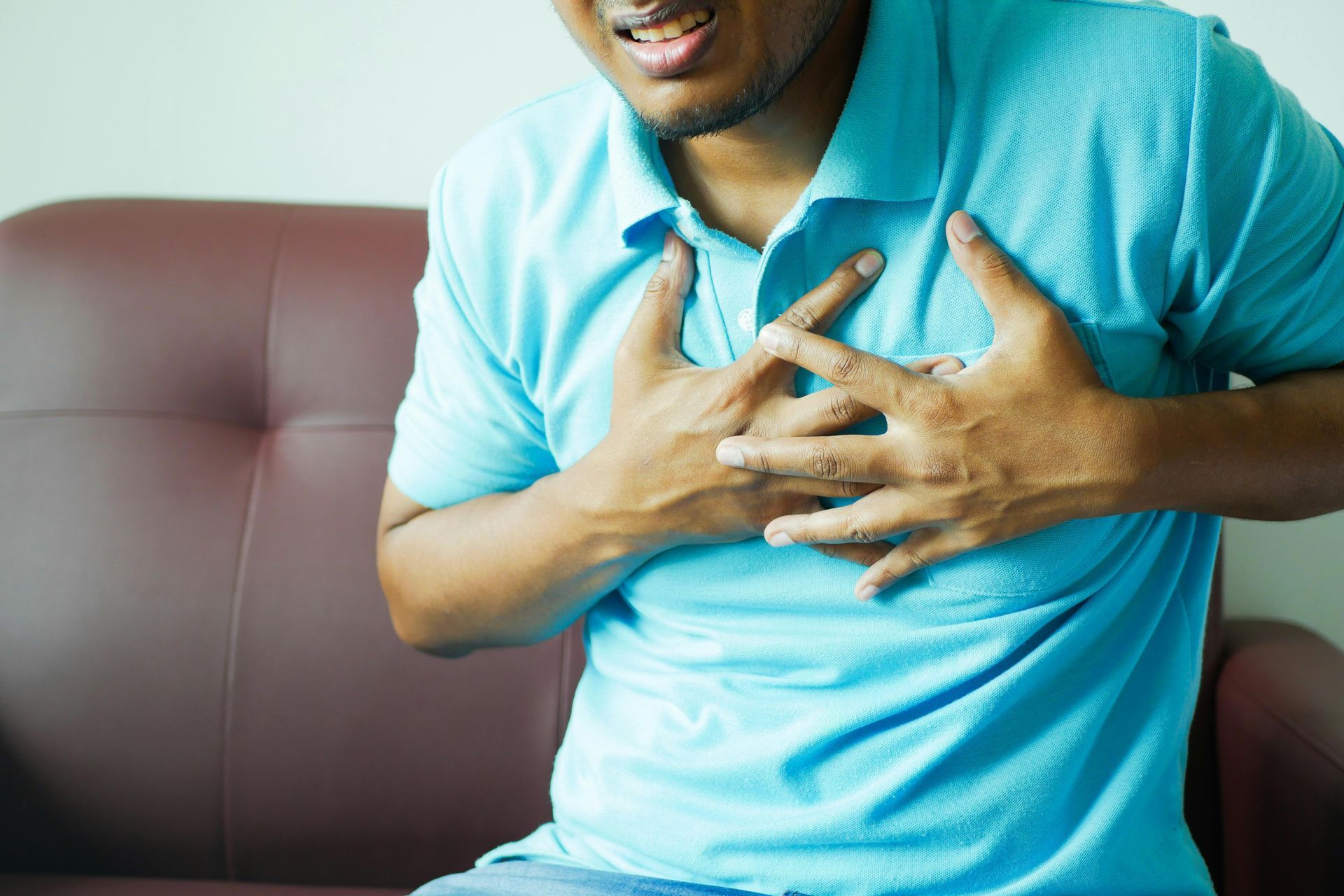

Heart Attack Signs and Symptoms from WEBMD.COM
Discomfort, pressure, heaviness, tightness, squeezing, or pain in your chest, arm, or below your breastbone
Discomfort that goes into your back, jaw, throat, or arm
Fullness, indigestion, or a choking feeling (it may feel like heartburn)
Sweating, upset stomach, vomiting, or dizziness
Serious weakness, anxiety, fatigue, or shortness of breath
Fast or uneven heartbeat (heart palpitations)
Anxiety
Heart attack symptoms can be different from person to person or from one heart attack to another. Women and people assigned female at birth are more likely to have these heart attack symptoms:
Unusual fatigue
Shortness of breath
Nausea or vomiting
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Discomfort in your gut (may feel like indigestion)
Discomfort in the neck, shoulder, or upper back
Trouble sleeping
With some heart attacks, you won’t notice any symptoms (a “silent” myocardial infarction). This is more common in people who have diabetes.
What does a heart attack feel like?
A heart attack feels like intense chest pain, the kind where someone is squeezing your chest really hard, or you're carrying a heavy weight on it. You could have this pain for a bit.
You might also feel weak, dizzy, or like you're going to pass out, and you could start sweating a lot. Sometimes, you'll also have mild pain in your jaw, neck, back, or arms. Plus, you may have trouble breathing.
What is a silent heart attack?
As the name suggests, a silent heart attack is one that happens without any obvious signs usually related to heart attacks, such as dizziness, a faster or irregular heartbeat (palpitations), trouble breathing, and anxiety. It’s hard for you to know if you’re having a silent heart attack because it happens without warning.

Stroke Signs and Symptoms from WEBMD.COM
Call 911 right away about signs of a stroke, which may include sudden:
Numbness or weakness of the body, especially on one side
Vision changes in one or both eyes, or trouble swallowing
Severe headache with an unknown cause
Problems with dizziness, walking, or balance
Confusion, trouble speaking or understanding others
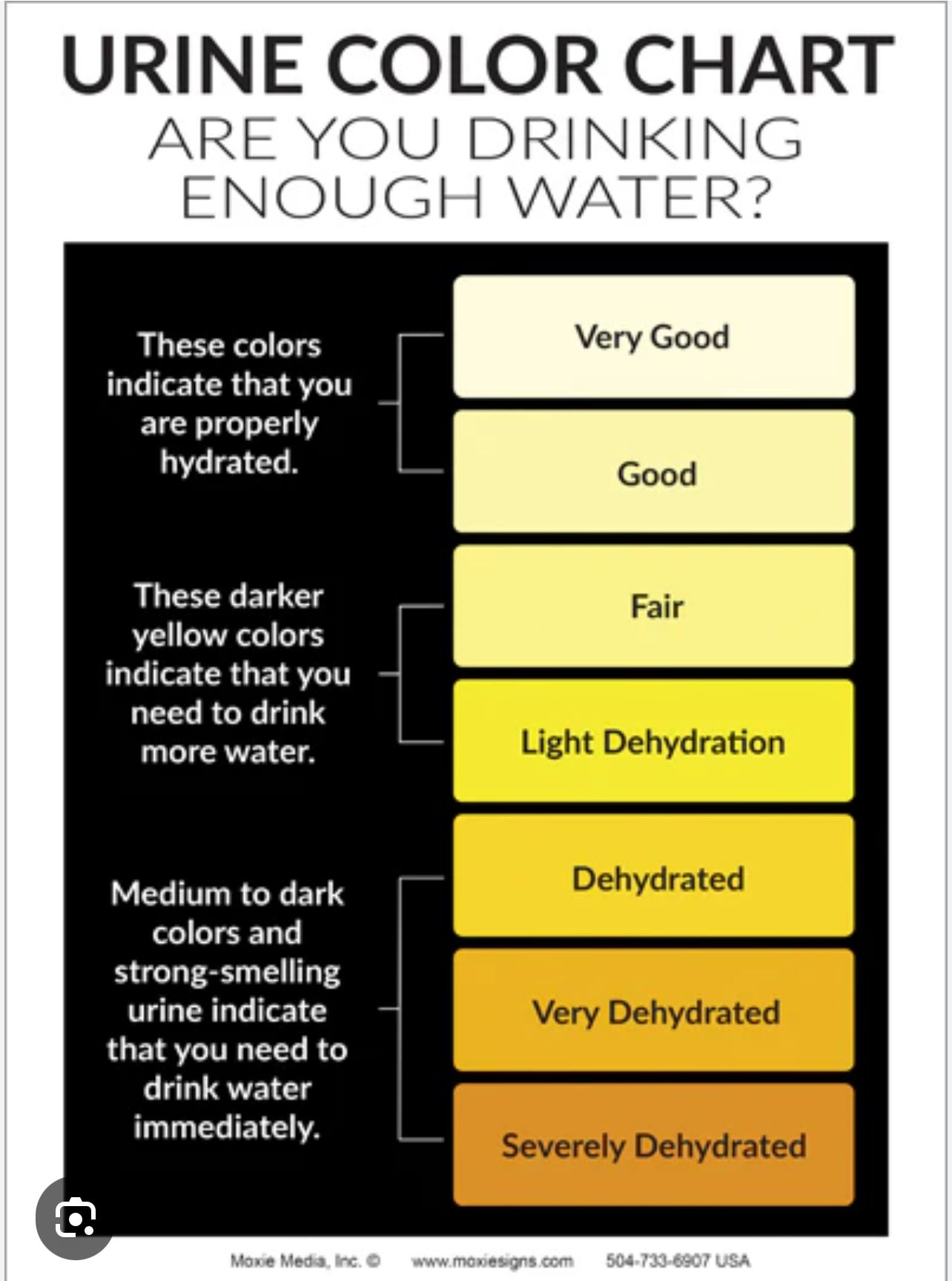
Info from WEBMD.COM
What Is Dehydration?
Dehydration happens when your body doesn't have as much fluid as it needs. That means your body can't function properly. Common causes include sweating, diarrhea, and vomiting.
You can have mild, moderate, or severe dehydration. If you are an adult, the seriousness of your dehydration depends on how much fluid your body is missing. In children, dehydration is based on how much body weight they've lost due to a lack of fluids.
Mild dehydration: This causes symptoms such as thirst, less peeing and sweating, and dry mouth. Children have mild dehydration when they lose 3%-5% of their body weight due to fluid loss. You can treat mild dehydration at home by drinking water, electrolyte drinks, or oral rehydration solutions you can buy at the drugstore.
Moderate dehydration: The symptoms are similar to those of moderate dehydration but are more intense. In children, it means they've lost 6%-10% of their body weight. You'll need a medical professional to give you fluids through an IV.
Severe dehydration: Symptoms include dizziness, sunken eyes, fainting, rapid breathing, and a racing heart. Children may lose over 10% of their body weight. This type of dehydration requires immediate medical attention. You may be treated with IV fluids containing salt.
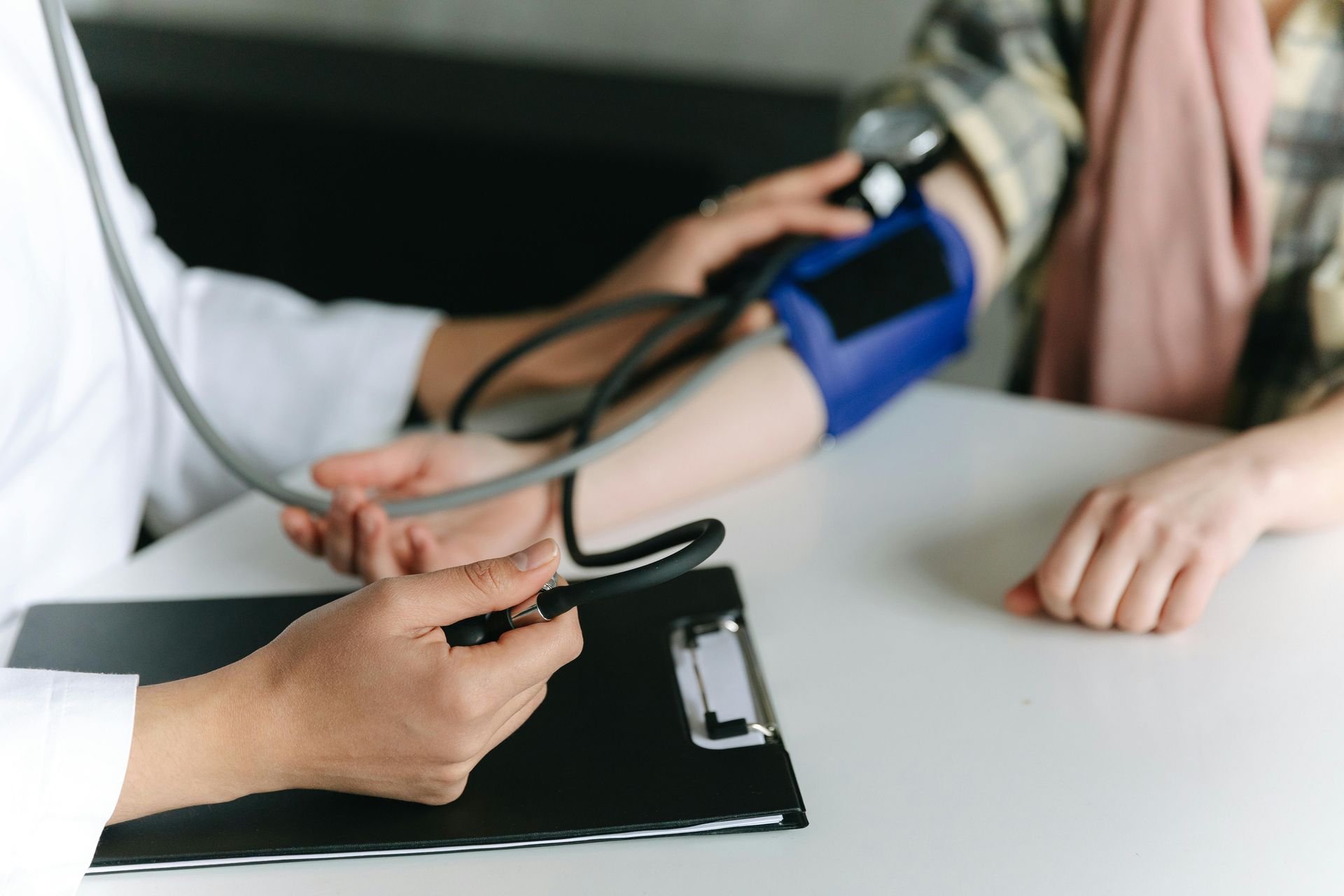
Test in the field
Systolic blood pressure. This first number measures the pressure of your blood against your arteries when it beats.
Diastolic blood pressure. This second number measures the pressure when your heart is resting between beats.
Interpreting your blood pressure measures:
Normal. Your blood pressure is normal when it's less than 120 over less than 80.
Elevated. Your blood pressure is elevated if the first number is 120-129 and the second number is less than 80.
Stage 1 hypertension. You have stage 1 hypertension if the first number of your blood pressure is 130-139 and the second number is 80-89.
Stage 2 hypertension. You have stage 2 hypertension if the first number is 140+ and the second number is 90+.
Hypertensive crisis. Your blood pressure reading is a number greater than 180 over a number greater than 120.
Normal variation in blood pressure
Normal blood pressure goes up from about 64/40 at birth to about 120/80 in a healthy adult. If someone were to take your blood pressure right after you gave a speech or jogged five miles, it'd probably be slightly high. This isn't necessarily cause for alarm: It's natural for blood pressure to rise and fall with changes in activity or emotional state.

What could it be?
If you or someone you know has sudden mental confusion, you need to see a doctor right away. It’s not normal, whether a person is young or old. Once you can figure out and treat the underlying cause, the confusion usually goes away.
What Are the Signs?
Symptoms can vary. Some people become quiet and withdrawn, while others get nervous and upset. They may:
Struggle to focus
Seem groggy, like they can’t wake up all the way
Mumble or say things that don’t make sense
Not recognize you or know where they are
Get worked up and upset for no reason
"See things that aren’t real
These symptoms will start suddenly. They may come and go or steadily get worse later in the day.
What Causes It?
Many conditions or health problems can cause sudden confusion, and some are more serious than others: They include:
Alcohol or drug abuse
Carbon monoxide poisoning
Very low amounts of sodium or calcium in your body
Diabetes (especially low blood sugar or high blood sugar levels)
Infections anywhere in the body (including the brain, lungs, and urinary tract). This is especially common for older people.
Medications (including drugs for pain, sleep, anxiety, depression, allergies, and asthma)
Pain (especially when a person gets too little or too much treatment)
Parkinson’s disease
Seizures
Strokes or “mini-strokes” (TIAs)
Other issues, like cancer and problems with the heart, kidneys, liver, lungs, and thyroid

